Inflammatory Bowel Disease – Looking at Crohn’s
In 1932, Burrill Bernard Crohn, an American gastroenterologist, found patients with inflammation of the terminal ileum; thus the disease was named for Crohn’s discovery.
According to the book, 100 Questions & Answers about Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis, the cause of these Inflammatory Bowel Diseases is unknown.
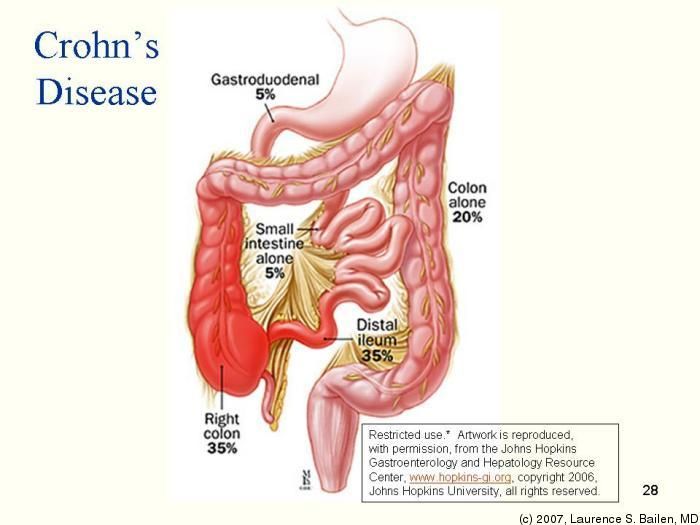
The difference between Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis is that Crohn’s Disease can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the anus. Ulcerative Colitis is found just in the rectum and colon.
These Inflammatory Bowel Diseases are a consequence of the disruption in the normal functioning of the immune System. Normally the immune system works to protect the body from foreign substances. According to Mayoclinc.com, most researchers “believe that some people with the disease develop it because of an abnormal immune response to bacteria that normally live in the intestine.”
The book, 100 Questions & Answers about Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis, says, “the immune system, for reasons that are unknown, directs its attacks against the gastrointestinal system.” This reaction that the immune system has is what causes the inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract and leading to the pain, diarrhea, and other ongoing symptoms.
Common symptoms of Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative Colitis are not only abdominal pain and diarrhea, but also, weight loss, poor appetite, fever, night sweats, rectal pain, and rectal bleeding. Also affect are joints, skin, and eyes. These diseases can lead to mal-absorption of vitamins and nutrients the body needs.
Crohn’s Disease effects 500,000 to 2 million people in the United States. Men and women are equally affected also. Inflammatory Bowel Disease can begin during adolescence and early adulthood most commonly. It can also begin in early childhood and later in life.
Although there is no cure for Crohn’s Disease or Ulcerative Colitis there are treatments with a goal in putting the disease in an inactive period called remission. Some treatments are anti-inflammatory agents such as 5-ASA compounds, corticosteroids, topical antibiotics, immuno-modulators, and other medications.
Sometimes surgery is an option for treatment. Because Crohn’s Disease can affect different parts of the intestines, infected parts can be removed. Some cases of Crohn’s Disease result in an ileostomy.
These diseases are not contagious, but Inflammatory Bowel Diseases can be embarrassing to talk about due to the symptoms.
There is no cure for Crohn’s Disease or Ulcerative Colitis but, there are new treatments being developed. Researchers are trying to gain a better understanding of these diseases to lead to more improved treatments.